Any business that involves shipping orders or warehousing will inevitably deal with packaging. Although it may seem like a straight-forward concept, packaging can come in various materials (such as primary, secondary, and tertiary) and types (such as sustainable and specialized options) to suit the unique needs of a business. Choosing the right packaging material is not just about ensuring product safety during transit but also about optimizing costs, improving sustainability, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
In this post, we will cover:
- The different types of packaging materials, including primary, secondary, tertiary, specialized, and sustainable options.
- The specific uses and benefits of each type of packaging material.
- Tips for choosing the right packaging based on your business needs.
Understanding Packaging Materials
Packaging materials are designed to protect products during storage, handling, and shipping. They play a vital role in maintaining product integrity and ensuring that goods reach customers in perfect condition. The choice of packaging material can affect everything from shipping costs to environmental impact, making it a critical consideration for businesses of all sizes.
Packaging materials are generally categorized into primary, secondary, and tertiary types:
- Primary packaging is the first layer of protection and directly encloses the product. It is often what the customer sees first, making it crucial for branding and product presentation.
- Secondary packaging groups individual products together, providing additional protection and facilitating easier handling and distribution.
- Tertiary packaging is used for bulk handling, storage, and transport, tertiary packaging includes items like pallets and crates that protect products during large-scale shipment.
Primary Types of Packaging
Primary packaging is the first line of defense for your products. It includes:
- Cardboard Boxes: Cardboard is widely used due to its versatility, lightweight nature, and cost-effectiveness. It comes in various forms such as corrugated boxes, which are ideal for shipping, and chipboard boxes, which are used for lighter items like cereal or cosmetics.
- Plastic Packaging: Plastics such as polyethylene and PET are commonly used for bags, containers, and bottles. Their durability and moisture resistance make them ideal for protecting products that need to stay dry and intact.
- Glass Packaging: Glass jars and bottles are commonly used in the food and beverage industry due to their ability to preserve products and their recyclability. However, they are heavier and more fragile than other packaging types, which can increase shipping costs.
- Metal Packaging: Metals like aluminum and steel are used in cans and tins, providing excellent protection for food, chemicals, and other products that require a strong barrier against contaminants.
Secondary Types of Packaging
Secondary packaging serves as an additional layer of protection and includes:
- Shrink Wrap: This material is commonly used to bundle products together or to secure items to pallets. Shrink wrap provides a tight seal, which helps protect products from dust and damage during transit.
- Labels and Tags: Essential for identifying products, labels and tags can include barcodes, product information, and compliance details. They are crucial for inventory management and customer communication.
- Paper Packaging: Kraft paper and tissue paper are used for void fill, wrapping, and as protective layers within boxes. Paper packaging is biodegradable and cost-effective, making it a popular choice for businesses focused on sustainability.
Tertiary Packaging
Tertiary packaging is essential for transporting large quantities of goods and includes:
- Pallets: Pallets, often made of wood or plastic, are used to stack and transport bulk goods. They make handling large quantities of products easier and more efficient.
- Crates: Crates provide robust protection for heavy or fragile items. They are reusable and come in various materials, including wood and plastic.
- Bulk Containers: Used for storing and transporting large volumes of materials, bulk containers offer efficiency and protection. They are ideal for industries that handle significant quantities of raw materials or finished goods.
Specialized Types of Packaging
Some products require specialized packaging to meet unique needs due to their specific characteristics, such as sensitivity to temperature, fragility, or susceptibility to environmental factors. Specialized packaging is designed to offer protection and ensure that these products maintain their integrity throughout the storage, handling, and shipping processes.
- Temperature-Controlled Packaging: This type of packaging, including insulated containers and gel packs, is crucial for transporting perishable goods like pharmaceuticals and food items that need to stay within a specific temperature range.
- Anti-Static Packaging: Used primarily for electronic components, anti-static packaging protects sensitive items from electrostatic discharge, which can damage electronic parts.
- Custom Packaging: Custom packaging solutions, such as branded boxes or uniquely shaped containers, help businesses stand out in the market and create a memorable customer experience.
Sustainable Types of Packaging Solutions
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, businesses are turning to eco-friendly packaging options. Sustainable packaging is not only good for the environment, but can also help reduce costs associated with packaging materials.
- Recyclable Packaging: Materials like certain plastics and glass can be recycled, reducing the environmental impact of packaging waste.
- Biodegradable Packaging: Compostable bags and paper products decompose naturally, making them an excellent choice for environmentally-conscious businesses.
- Reusable Packaging: Packaging that can be used multiple times, such as bulk containers and reusable bags, helps reduce waste and can offer cost savings over time.
Choosing the Right Packaging Material
Selecting the right packaging material depends on various factors, including the type of product, shipping method, storage conditions, and cost-effectiveness. For instance, a business that ships fragile items might prioritize packaging materials that offer superior protection, such as bubble wrap and sturdy boxes, while a company focused on sustainability might opt for biodegradable or reusable packaging solutions. Custom packaging options are a great way to select the perfect materials for your business needs whilst providing a unique customer experience.
By carefully considering the factors that go into packaging, businesses can choose options that not only protects their products but also aligns with their brand values and operational goals. Whether it’s ensuring safe delivery, enhancing customer experience, or minimizing environmental impact, the right packaging choice can make a significant difference in your business’s success.
The ability to effectively prioritize orders is a critical aspect in running a small or medium-sized business. Effective order prioritization not only enhances operational efficiency but also plays a significant role in keeping customers satisfied. Whether you’re handling a few dozen orders or managing a higher volume of purchases, the right prioritization strategy can make a substantial difference in how smoothly your business runs and how many of your customers buy again.
In this post, we will cover:
- The fundamental methods of order prioritization, including FIFO and FEFO, and how they impact business efficiency.
- Advanced techniques like the Eisenhower Matrix and WSJF for optimizing order handling in more complex scenarios.
- The role of technology in automating and streamlining order prioritization, along with best practices for improving order processing workflows.
What is Order Prioritization?
Order prioritization involves fulfilling orders in a sequence that aligns with your business’s operational goals and customer expectations. By determining which orders to process first, businesses can allocate resources more effectively, avoid shipping delays, and maintain a high level of customer satisfaction. For instance, when managing a large batch of orders, knowing which ones to prioritize can help prevent delays and ensure that the most urgent shipments are dispatched promptly.
The way in which your business priorities orders will depend on various factors. Order urgency, shipping options, order value, holiday deadlines, stock availability, product shelf-life, and customer type can all impact order priority depending on the nature of your business.
Consider a scenario where an e-commerce business faces a surge in orders during a holiday season. Without proper prioritization, high-priority orders expected to be delivered before the holiday could be delayed, leading to dissatisfied customers and potential loss of business. Implementing a structured approach to order prioritization helps businesses navigate such challenges and streamline fulfillment and shipping processes.
Understanding the Basic Methods of Order Prioritization
Order prioritization strategies aren’t a one-size-fits-all; there are various strategies which will each work better for different businesses and customer expectation:
- First In, First Out (FIFO): This method processes orders in the order they were received, ensuring that older orders are fulfilled first. FIFO is particularly useful for maintaining a fair and transparent order handling process, preventing any backlog.
- Earliest Due Date: This technique focuses on fulfilling orders with the earliest promised delivery dates first, which is crucial when dealing with time-sensitive shipments. Prioritizing based on due dates helps ensure that important customers receive their orders as expected.
- First Expired, First Out (FEFO): Especially relevant for industries such as food and cosmetics, FEFO prioritizes orders based on product expiration dates, ensuring that items nearing their expiry are shipped out first. This method helps minimize waste and ensures customers receive fresh products.
Advanced Prioritization Techniques
For businesses seeking to refine their order prioritization further, advanced techniques such as the Eisenhower Matrix and Weighted Shortest Job First (WSJF) offer valuable frameworks:
- The Eisenhower Matrix: This tool helps distinguish between urgent and important tasks, allowing businesses to prioritize orders based on their criticality and impact. By categorizing orders into urgent-important, urgent-not important, not urgent-important, and not urgent-not important, businesses can allocate resources more effectively.
- Weighted Shortest Job First (WSJF): This technique prioritizes orders by assessing the cost of delay against the size of the job. By focusing on high-impact orders that can be completed quickly, businesses can maximize efficiency and customer satisfaction.
These advanced methods are particularly beneficial in complex operational environments where simple FIFO or due date-based prioritization may not be sufficient.
Leveraging Technology for Effective Order Prioritization
Technology plays a crucial role in modern order prioritization. Order Management Systems (OMS) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems can automate the prioritization process by integrating real-time data on inventory levels, order status, and customer preferences. These systems allow businesses to streamline order processing, reduce manual errors, and ensure that resources are allocated where they are needed most.
For example, an OMS can automatically prioritize orders based on criteria such as shipping method, customer type, or order size, ensuring that high-priority orders are processed first. This automation not only saves time but also helps businesses maintain a consistent level of service even during peak periods.
Best Practices for Order Processing Workflows
No matter the prioritization strategy or combination of strategies you chose for your business, there are several best practices to keep in mind when it comes to building an order processing workflow.
Practices such as batch picking and zone picking can streamline the fulfillment process and reduce the time required to complete orders. Batch picking, where multiple orders are picked simultaneously, reduces the number of trips needed to fulfill orders. Zone picking on the other hand involves assigning pickers to specific areas of the warehouse, minimizing movement and increasing productivity.
Establish clear guidelines and criteria for prioritizing orders. For example, high-value orders, recurring customers, or orders with strict deadlines might be prioritized over others. Consistent rules help ensure that all team members are aligned on which orders need to go out first.
When planning your fulfillment schedule, include buffer time for high-priority orders to account for potential delays. This helps ensure that important orders are delivered on time, even if unexpected issues arise in fulfillment or shipping.
Continual Improvement in Order Prioritization
Order prioritization is not a one-time task but an ongoing process that requires regular evaluation and adjustment. Use customer feedback to refine your prioritization processes. If customers frequently mention delayed deliveries or frequent customers are becoming dissatisfied, adjust your prioritization criteria to address these concerns. As business needs and market conditions change, your prioritization strategies should be flexible enough to evolve as well.
Predictive analytics is another way you can continuously improve your order prioritization. Historic order and customer data can be used to forecast which orders are likely to become urgent. By anticipating future bottlenecks and order urgency, you can adjust your prioritization strategy in advance to avoid delays.
Ultimately, the goal is to balance operational efficiency with customer expectations, ensuring that every order is fulfilled in a timely and organized manner. With the right approach, order prioritization can become a powerful tool in your business’s overall strategy for success.
For small and medium-sized businesses that rely on timely shipments, understanding the factors that influence delivery times between ZIP codes is critical for customer satisfaction.
In this post, we will cover:
- The mechanics of the ZIP code system and its role in efficient mail delivery.
- Factors influencing ZIP code delivery times, including distance, weather, and service type.
- Strategies for small businesses to optimize their shipping processes for better delivery outcomes.
How ZIP Codes Work
The ZIP code system, introduced by the United States Postal Service (USPS) in 1963, plays a vital role in sorting and delivering mail. ZIP codes are composed of five digits, with the first digit representing a group of U.S. states, the next two digits pinpointing a region or large city, and the last two digits identifying a specific post office or area.
For example, consider the ZIP code:
90210
- The first digit, 9, indicates the western states group
- The next two digits, 02, point to a specific region within California
- The last two digits, 10, designate a particular post office in Beverly Hills.
Overall, the ZIP code system helps efficiently route mail to its correct destination by breaking down locations into regions, cities, and specific areas.
What is ZIP Code Delivery Time?
ZIP code delivery time refers to the period it takes for mail to travel from one ZIP code to another. This time frame is crucial for businesses, as it affects how quickly products can reach customers across the country. Several factors influence delivery times, including the distance between ZIP codes, weather conditions, and the type of postal service used. For instance, First-Class Mail typically arrives within 1-5 business days, while Priority Mail may offer faster delivery for a slightly higher cost.
The ZIP to ZIP Mail Delivery Process
The ZIP to ZIP mail delivery process involves several key steps that streamline mail handling and ensure parcels end up in the right place. First, mail is collected from various drop-off points and sorted at local postal facilities based on the destination ZIP codes. The mail is then transported to regional sorting centers, where it is further organized by ZIP code regions. Finally, the sorted mail is dispatched to the appropriate local post offices for final delivery to the customer.
Factors That Affect ZIP to ZIP Delivery Time
Understanding the factors that affect ZIP to ZIP delivery times can help businesses optimize their mailing strategies. Key factors include:
- Federal Holidays: These can delay mail as the couriers may not operate on these days.
- Backlog of Direct Mail: High volumes of mail can slow down processing times.
- Weather Conditions: Severe weather can disrupt transportation routes, leading to delays.
- Distance: Naturally, the greater the distance between two ZIP codes, the longer the delivery time.
USPS Mail Pick Up Times
Mail pick-up times, or the times when mail is collected from USPS drop-off points, are crucial in the delivery timeline. Knowing these times helps in planning when to send out mail to ensure it enters the postal system as soon as possible. You can find local pick-up times via the USPS website or by visiting your nearest post office.
Estimating Delivery Times
The USPS delivery time calculator can be used to estimate delivery times between ZIP codes. This tool provides estimates based on the origin and destination ZIP codes, as well as the chosen mail service. Here’s an overview of different USPS services and their typical delivery times:
- First-Class Mail: 1-5 business days, suitable for small packages up to 13 ounces.
- Priority Mail: 1-3 business days, offers a balance of speed and cost for most packages.
- Priority Mail Express: Overnight to 2-day delivery, ideal for urgent shipments.
- Parcel Select Ground: 2-8 business days, a cost-effective option for less time-sensitive deliveries.
Suppose you were a business based in Atlanta (30301) shipping a package to a customer located in Beverly Hills (90210) via USPS Priority Mail, it would usually take around two days for the delivery to arrive.
Common ZIP Code To ZIP Code Delivery Challenges
Several challenges can affect delivery times between ZIP codes:
- Geographical Factors: Remote locations often experience longer delivery times due to fewer postal facilities or transportation routes.
- Peak Seasons: Holidays can significantly impact delivery times due to increased mail volumes. Businesses should plan accordingly and be transparent with customers during holiday seasons.
- Accurate Addressing: Ensuring addresses are correct and complete can prevent mail from being delayed or returned.
Being transparent with customers about shipping times and ensuring addresses are complete before sending orders can help businesses overcome these challenges and keep customers satisfied.
Shipping Tips for Small and Medium-Sized Businesses
To streamline shipping and improve delivery times, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) can consider the following strategies:
- Optimize Shipping Processes: Shipping programs can be used to automate order delivery, allowing shipping to be managed more efficiently.
- Warehouse Strategically: Consider warehousing inventory in strategic locations closer to major customer bases to speed up delivery and minimize costs.
- Plan for Holidays: Ensure items ordered before big holidays will arrive on time and be transparent with customers on when they can expect their parcels.
- Keep Customers Informed: Provide regular updates on order status via email or SMS, including expected delivery times. If delays occur, notify customers promptly to manage expectations.
- Choose the Right USPS Service: Evaluate the urgency and value of each shipment to select the appropriate USPS service. For urgent or high-value shipments, use Priority Mail Express, while Parcel Select Ground offers a cost-effective solution for less time-sensitive items.
Knowing how ZIP codes work, the factors affecting delivery times, and how to optimize the shipping process can help businesses plan better and communicate more effectively with customers. Using tools such as the USPS delivery time calculator, selecting the appropriate USPS service, and warehousing inventory strategically to reduce shipping distance, are great strategies for gaining more transparency and control over shipping times. At the end of the day, customers don’t want to be left in the dark about when they can expect to receive their order, so understanding mail delivery times from ZIP code to ZIP Code is a must for any business.
Mail Delivery Time ZIP Code To ZIP Code Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How accurate are USPS delivery estimates?
USPS estimates are generally reliable, with 91.4% of First-Class Mail delivered on time, but can be affected by unforeseen factors like weather or holidays (USPS).
Can I track my mail delivery between ZIP codes?
Yes, most USPS services offer tracking features, allowing businesses to monitor their mail’s progress.
How Long Does Mail Take From ZIP Code to ZIP Code?
This depends on the distance, service type, and other factors mentioned earlier. Typically, First-Class Mail takes 1-3 days, while Priority Mail can be faster.
How Long Does Stamped Letter Delivery Take?
Stamped letters sent via First-Class Mail generally arrive within 1-3 business days.
Shipping plays a crucial role in the success of ecommerce businesses, but the logistics involved can often be complex and confusing. One of the key aspects of shipping logistics is understanding shipping zones.
In this post, we will cover:
- The definition and importance of shipping zones and how they affect logistics and delivery times.
- Detailed comparisons of shipping zones across major carriers like USPS, FedEx, and UPS.
- Strategies to optimize shipping processes for cost efficiency and improved delivery speeds.
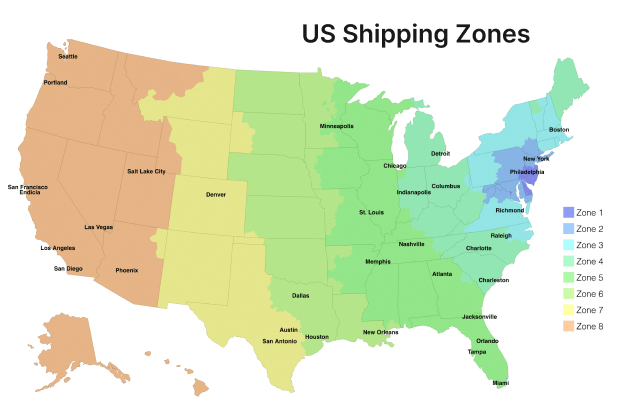
What are shipping zones?
Shipping zones are geographical areas defined by shipping companies to facilitate the management of delivery times and calculation of shipping costs. Spanning from Zone 1 to Zone 8 for domestic shipments in the United States, these zones are determined not by the actual miles traveled but rather through groupings of ZIP codes from the shipment’s point of origin to its destination. Understanding these zones is crucial for effectively managing shipping costs and ensuring timely deliveries.
How to calculate shipping zones
Calculating shipping zones might initially seem daunting, but it becomes straightforward once you grasp the basics. The primary basis for determining shipping zones is the distance from the shipping origin point to the destination. This distance doesn’t refer to the direct mileage but rather to the grouping of ZIP codes into specific zones defined by shipping carriers.
Shipping carriers such as USPS, FedEx, and UPS have mapped out the United States into various zones, starting from the shipping origin (Zone 1) and extending outward. The farther the destination ZIP code from the origin, the higher the zone number.
Suppose your business is located in Chicago, Illinois, and you need to ship a package to Miami, Florida. Here’s how you might determine the shipping zone:
- Identify the origin ZIP code: For example, 60601 (Chicago).
- Identify the destination ZIP code: For example, 33101 (Miami).
- Use a shipping zone chart or online calculator provided by your carrier. Most carriers offer tools on their websites where you can input the origin and destination ZIP codes to find out the shipping zone.
- Check the result: The tool calculates and displays the zone, which for this example might be Zone 5.
Understanding how to calculate shipping zones allows businesses to estimate shipping costs more accurately and plan their logistics accordingly.
FedEx, UPS, USPS Shipping Zones: What Are They?
For practical purposes, shipping zones vary slightly between carriers but generally follow a similar pattern. Here’s a basic table to help estimate your shipping zones for USPS, UPS, and FedEx (updated June 2024):
| Shipping Zone | Mile Radius (from origin) |
|---|---|
| Zone 1 (local) | 50 mile radius |
| Zone 2 | 51 – 150 mile radius |
| Zone 3 | 151 – 300 mile radius |
| Zone 4 | 301 – 600 mile radius |
| Zone 5 | 601 – 1000 mile radius |
| Zone 6 | 1001 – 1400 mile radius |
| Zone 7 | 1401 – 1800 mile radius |
| Zone 8 | 1801+ mile radius |
| Zone 9 | Freely Associated States |
For those looking to dive deeper into shipping zones and how they’re calculated by different carriers, here are some useful resources:
- USPS Domestic Zone Charts: This tool allows you to determine the shipping zone for your USPS shipments based on zip codes.
- UPS Shipping Costs and Rates: Explore detailed information about UPS shipping costs and how they vary by zone and service type.
- FedEx Zip Code Shipping Zone Tool: A quick and easy tool to find out shipping zones based on zip codes specifically for FedEx shipments.
These resources provide valuable insights and tools to help you better understand and manage your shipping operations.
Key Factors That Define Shipping Zones
Several factors come into play when defining shipping zones, each contributing to how shipping costs are calculated and delivery times are estimated. Here are the key factors that carriers consider:
- Geographic Boundaries: The primary factor, which includes the physical distance measured by zones, starting from the shipment’s origin.
- Origin Point: The specific starting location of a shipment, crucial for determining the initial zone and the consequent zones a package will pass through.
- Destination Point: The endpoint of the shipment journey, which, along with the origin, helps to define the exact zone category.
- Carrier-Specific Rules: Each carrier may have unique rules or additional factors, such as regional regulations or special zones for remote areas.
Understanding these factors can help businesses optimize their shipping strategies by choosing the most cost-effective options and improving delivery accuracy.
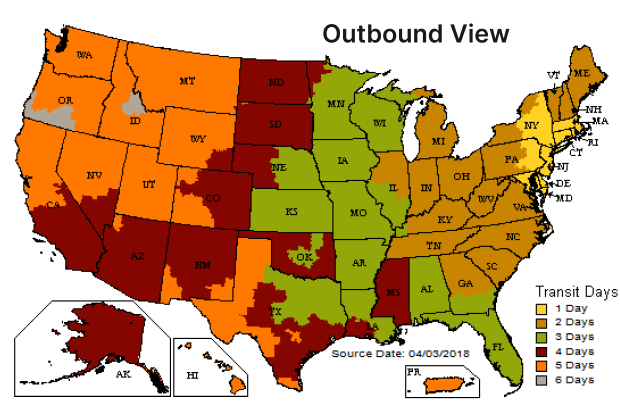
The Role of Shipping Zones in Freight and Parcel Delivery
Shipping zones significantly influence both freight and parcel delivery, impacting the logistics, cost, and strategy behind each type of shipment. Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses to optimize their delivery options and manage costs effectively.
Freight vs. Parcel Delivery:
- Freight Shipping: Involves transporting large quantities of goods, typically organized on pallets or in containers, and is facilitated by larger vehicles such as trucks, ships, or planes. Freight shipments are more complex due to the scale and the logistics required, such as route planning, load balancing, and managing delivery schedules. Shipping zones affect freight shipping primarily in terms of cost calculation and delivery time management. The farther the goods need to travel across zones, the higher the cost and potential for longer delivery times.
- Parcel Delivery: More common for small business and personal shipments, parcel delivery involves smaller, often individually packaged items. This type of delivery is generally quicker and involves less complex logistics than freight. However, shipping zones are still a critical factor, as they directly influence the cost and speed of delivery. For instance, a parcel shipped within the same or a nearby zone will typically arrive faster and cost less compared to one sent to a distant zone.
Shipping zones help businesses and logistics managers make informed decisions about shipping methods, costs, and prioritization of deliveries based on distance. For example, businesses can choose to warehouse inventory in strategic locations closer to their major customer bases to reduce the distance parcels or freight need to travel, thus minimizing costs and speeding up delivery.
How do shipping zones affect shipping costs?
Shipping zones significantly influence shipping costs, as they are largely determined by the distance a shipment travels and its zone classification. A thorough understanding of this dynamic is crucial for businesses to optimize their shipping strategies for cost-efficiency.
Zone number
Zone numbers are assigned based on the distance from the shipment’s origin. The greater the distance to the destination, the higher the zone number, which generally results in increased shipping costs.
To mitigate these costs, businesses can strategically locate inventory closer to key markets or consolidate shipments to reduce the number of zone crossings.
Order Weight
The weight of an order significantly influences shipping costs across different zones. Carriers typically categorize shipments into weight brackets, with each bracket having specific cost implications that increase with the distance covered. Let’s use the chart below as an example to illustrate how weight impacts shipping costs in various zones.
| Shipping Zones | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pounds | 1&2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | |
| 1 | $6.70 | $7.15 | $7.30 | $7.45 | $7.60 | $7.85 | $8.45 | $10.60 | |
| 2 | $7.25 | $7.70 | $8.75 | $9.85 | $10.65 | $11.80 | $12.90 | $16.85 | |
| 3 | $7.90 | $8.85 | $10.15 | $11.75 | $13.35 | $14.65 | $17.30 | $22.55 | |
For instance, consider a shipment weighing 3 pounds. According to the chart, if this package is shipped within Zones 1 and 2, the cost might be $7.90. However, if the same package is shipped to Zone 9, the cost escalates to $22.55. This example clearly shows the direct relationship between weight, zone distance, and shipping cost.
To manage and potentially reduce shipping costs, businesses should consider packaging strategies that minimize weight. Using lighter packing materials and optimizing package dimensions can effectively lower the total weight of shipments, thus reducing costs across all zones.
How can ecommerce companies afford to offer free shipping?
Free shipping is a popular marketing tool used to attract customers, but it can be costly for businesses. This section explores how companies manage to offer this perk.
Businesses often absorb the shipping cost into the product price or set minimum order thresholds to balance the cost of offering free shipping. They may also use economical packaging and optimize their shipping zones to reduce expenses.
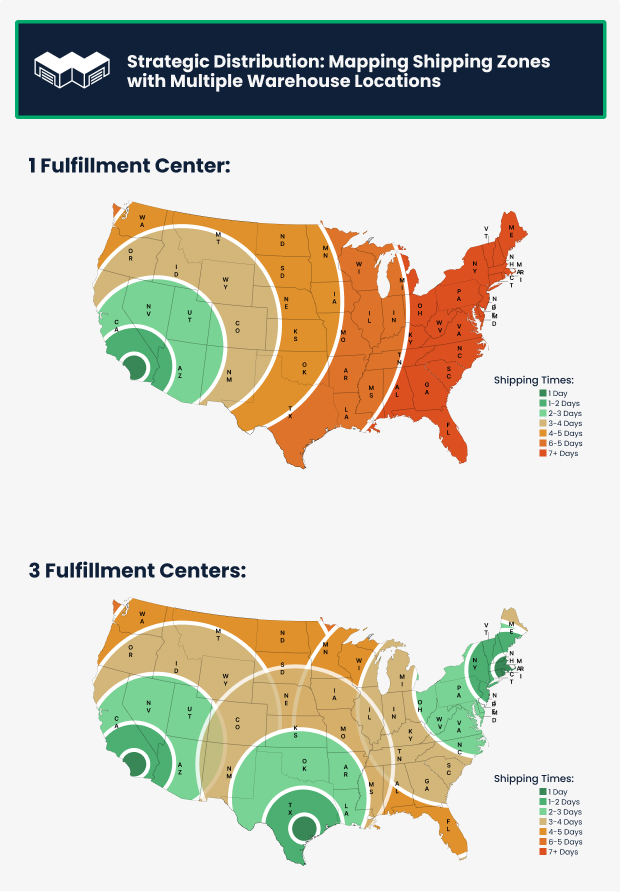
How to reduce shipping costs and transit times
Minimizing shipping costs while also improving delivery speeds is a crucial challenge for small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The demand for rapid and economical delivery options is high—nearly three-quarters of consumers expect deliveries to be fast and affordable, and over a fifth may abandon their cart if shipping is too slow.
Additionally, the tolerance for waiting has decreased significantly; the average acceptable delivery time is now just over four days, down from 5.5 days a decade ago. This shift is part of a broader trend where e-commerce’s share of global retail sales is anticipated to climb, potentially accounting for 22% by 2023. These trends underline the need for businesses to optimize their logistics operations effectively.
Strategic use of small warehouse spaces, such as those offered by companies like WareSpace, can be a game-changer in meeting these expectations, providing solutions that allow for quicker, more cost-effective shipping methods.

Tour a small warehouse space TODAY!
See how a small warehouse space can transform your businesses.
By renting small warehouse spaces in strategic locations, businesses can significantly alter their shipping dynamics. This proximity to customers reduces the number of shipping zones a package travels through, lowering shipping costs and speeding up delivery times.
For SMEs, this is a cost-effective alternative to owning multiple warehouses across the country. Instead of substantial investments in property and infrastructure, renting small spaces offers flexibility and scalability.
By understanding and implementing these strategic approaches, businesses can leverage small warehouse spaces like those offered by WareSpace to optimize their shipping operations. This not only reduces costs and enhances delivery speeds but also improves overall customer satisfaction, making it a win-win for growing businesses.
Interested in small warehouse spaces for rent as a solution for your shipping zones? Book a tour today to visit one of our locations in ideal spots around the US and see firsthand how WareSpace can help streamline your shipping processes and reduce costs.
In an era of rapid online growth and changing business dynamics, the warehousing landscape has experienced a pivotal shift in the USA. Traditional warehousing, with its expansive space and vast inventories, served industries well in the past. However, as the business climate evolves, there’s an evident shift from large warehouses to more sustainable, small warehouse spaces that offer the same benefits as their larger counterparts. This shift is not just about downsizing but about adapting to the needs of an agile market.
Defining Small Warehousing
Historically, the warehousing industry has been dominated by vast spaces—gigantic repositories where goods from different parts of the world congregated. However, the times are changing. A transition from these large storage facilities to more compact, efficient spaces is becoming increasingly noticeable. But what marks this shift?
In the logistics world, small warehouses represent adaptability and agility. Unlike their massive counterparts, which are cumbersome and often inflexible, these spaces align more closely with the evolving needs of modern businesses. To learn more about small warehouses, visit our ‘Explore our Spaces‘ page.
The Rise of Small Business and Technology’s Role in Enabling It
With the consistent growth of small and medium businesses in the USA, the demand for operational efficiency has skyrocketed. Technology has played a pivotal role in this surge. Sophisticated inventory management systems, AI-driven forecasting tools, and other tech solutions have empowered smaller businesses to compete in a crowded marketplace. This advancement has fostered a symbiotic relationship with the rise of small warehousing.
- Growing SMB Landscape: The USA has seen a steady rise in small to medium businesses, driven by innovation and niche market solutions.
- Technology’s Influence: Advanced tools enable these businesses to predict demands, manage their stocks efficiently, and ensure swift deliveries—making small warehousing a feasible solution.
The intertwining growth of technology and small-to-medium businesses in the USA is undeniably shaping the future of any business, online or not. As technology continues to break barriers and democratize access to sophisticated tools, even the smallest of businesses can now operate with an efficiency previously reserved for giants.
Small warehousing, a trend emerging hand in hand with these developments, showcases how adaptable and resilient the US business landscape is becoming. By leveraging this powerful combination of technological advancement and strategic warehousing, SMBs are poised to define the next era of American business.
Why the USA is Embracing Small Warehouses
The USA’s business paradigm, coupled with increasing online demands, has drastically changed over the past decade. The need for businesses to be closer to their customer base has made small warehousing a sought-after solution.
- E-Commerce Explosion: The rapid growth of online shopping means customers expect quicker deliveries. Small warehouses, strategically placed, can cater to this demand.
- Multiple Distribution Points: With a dispersed customer base, having multiple distribution points ensures businesses can meet varying demands swiftly.
The transformation of the business landscape in the USA, accelerated by e-commerce, calls for strategic adaptability. Small warehouses stand as a testament to this evolution, bridging the gap between businesses and their geographically diverse customers. As businesses continue to navigate the expectations of the modern consumer, it’s clear that embracing small warehousing isn’t just a trend—it’s a forward-thinking approach to ensuring sustained growth and customer satisfaction in the ever-evolving American market.
Benefits of Opting for Small Warehouse Space in the US
In recent years, many businesses have been reevaluating their logistical needs, discovering the multifaceted advantages of smaller warehouse spaces. From heightened cost efficiency to more personalized customer interactions, these compact storage solutions are not just about saving space; they’re about enhancing every aspect of the supply chain.
Let’s delve into the specific benefits that small warehouse spaces in the US bring to the table for businesses, especially those looking to gain an edge in today’s competitive market.
Faster Fulfillment & Delivery
In the age of next-day or even same-day deliveries, the emphasis on speed cannot be overstated. Small warehouses, typically located closer to urban centers or customer clusters, offer:
- Swift Movement: Reduced travel distances mean faster deliveries.
- Adaptability: Quick adjustments to shifting market trends and emerging consumer demands ensure businesses remain agile.
These factors combine to make small warehouses the linchpin of modern, efficient supply chains.
Cost Efficiency
One of the primary reasons businesses are leaning towards smaller warehouse spaces is the considerable cost-saving potential. When compared to the larger, traditional warehouse spaces, the rental costs of smaller facilities are significantly more affordable. But the savings don’t stop there. Operating a smaller space naturally leads to a reduction in utility bills and general upkeep costs. These combined savings can make a substantial difference in the bottom line for businesses, especially those in their formative years or those looking to optimize operational expenses.
If you are looking for efficient and cost-effective small warehouses, visit our locations page.
Flexibility and Scalability
The business landscape is anything but static. Demand can fluctuate based on a myriad of factors, from seasonal changes to sudden promotional activities. Small warehouses offer businesses the agility to scale their operations up or down based on these fluctuating needs. Instead of being tied down to a large space (and its associated costs) during slower periods, businesses can optimize their storage needs in real-time.
This flexibility ensures they’re always primed to take advantage of peak periods without being burdened during lulls.
Improved Inventory Management
Inventory management is a balancing act, and small warehouses facilitate:
- Enhanced Oversight: Concentrated space allows for meticulous monitoring of stock levels.
- Balance: Minimize risks associated with overstocking or understocking, ensuring optimal inventory levels.
Effective inventory management not only optimizes storage but also fortifies the trust businesses build with their customers.
Personalized Customer Service
Proximity to consumers provides businesses with a competitive edge:
- Regional Insights: Being close to the market offers a better understanding of regional trends and preferences.
- Tailored Offerings: The ability to adapt products or services based on the specific demands of the local populace.
Harnessing these advantages allows businesses to foster deeper, more meaningful connections with their clientele.
The Future of Small Warehousing in the USA
The trajectory of small warehousing in the USA is not just a fleeting trend—it’s shaping up to be the future of logistics and commerce. As businesses continually prioritize agility, efficiency, and a customer-centric approach, the importance of these compact storage solutions grows exponentially.
These factors indicate that the future of small warehousing in the USA is not just promising—it’s pivotal. Businesses that adapt to this shift and maximize their potential are positioning themselves for success in a rapidly changing commercial landscape.
Hyper-Local Strategie
The push for hyper-local strategies is clear. Businesses are realizing the value of connecting with local communities, understanding regional nuances, and delivering tailored experiences. Small warehouses, by virtue of their size and strategic placements, will be central to executing these hyper-local strategies.
Rapid Response Times
In an age where immediacy is increasingly becoming a consumer expectation, the ability to quickly process and ship out orders is crucial. Small warehouses, especially when dispersed across key locations, allow businesses to cut down delivery times significantly, ensuring that customer satisfaction remains high.
Environmental Considerations
The sustainability angle is also worth noting. Smaller warehouses, when operated efficiently, have the potential to leave a reduced carbon footprint, especially when considering shorter transportation routes and optimized energy usage. As more businesses become environmentally conscious, this could be another driving factor in the rise of small warehousing.
Pioneering the Future with Small Warehousing Solutions
The rise of small warehousing in the US signifies a larger shift in the business landscape—a move towards agility, efficiency, and customer focus. As businesses in the USA continue to evolve, embracing small warehouses might just be the key to unlocking unparalleled operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. If you’re a business aiming to edge ahead in this competitive market, it’s time to consider the multifaceted benefits of small warehousing in your operations.
Are you interested in seeing how a small warehouse could enhance your business? Book a tour to visit one of our many conveniently located facilities across the US, or speak with one of our experts.
